Road accident deaths in India number the highest in the world. The Global status report on road safety 2013 estimates that more than 231 000 people are killed in road traffic crashes in India every year. To bring this figure in control enhancement of safety is required to be increased at all technological, judiciary & public awareness levels. Lets explore the technological part in the article ahead.
 Road Safety is a very basic topic and in schools we all have been taught about basic traffic rules, to ensure safety of ourselves & others on the road, But imagine an early foggy morning or a traffic signal failure in mid-night or driving a car on 150km/h, at this point tracing of a road signal or keeping an eye on the road traffic is quite impossible. Now road safety technology comes to the picture to automatically assist the driver on the road. Road Safety Technologies are some of the high-tech communication & alarm systems available with us now a day to enhance driver & pedestrians’ safety on roads. A road safety system could be installed in a car, helping driver on road by guiding them about fore-coming vehicles, road diversion, on way coming people or any animal and could be upgraded with cameras, sensors, navigation systems or it can be a centralized vehicle to vehicle system or a satellite monitoring system. In this article we will be mentioning some of the innovations coming up globally to enhance road safety and its driving factors in Indian traffic scenario. Further to that our next generation cars have self-driving technology, will that adds to road safety or new challenges will add-on. Let’s find out.
Road Safety is a very basic topic and in schools we all have been taught about basic traffic rules, to ensure safety of ourselves & others on the road, But imagine an early foggy morning or a traffic signal failure in mid-night or driving a car on 150km/h, at this point tracing of a road signal or keeping an eye on the road traffic is quite impossible. Now road safety technology comes to the picture to automatically assist the driver on the road. Road Safety Technologies are some of the high-tech communication & alarm systems available with us now a day to enhance driver & pedestrians’ safety on roads. A road safety system could be installed in a car, helping driver on road by guiding them about fore-coming vehicles, road diversion, on way coming people or any animal and could be upgraded with cameras, sensors, navigation systems or it can be a centralized vehicle to vehicle system or a satellite monitoring system. In this article we will be mentioning some of the innovations coming up globally to enhance road safety and its driving factors in Indian traffic scenario. Further to that our next generation cars have self-driving technology, will that adds to road safety or new challenges will add-on. Let’s find out.
Technologies on Road
The very basic traffic management technology we all familiar with is Red Light Signal. But this signal seems no more sufficient to manage heavy traffic and fast running vehicles to the sudden on way obstacles or road diversions ahead. So road safety technologies are now available worldwide to help out drivers & other people on road to drive & ensure safety & security or road traffic. Some of the road technologies available now-days are:
1) In-vehicle navigation system with GPS and TMC for providing up-to-date traffic information.
2) Adaptive cruise control (ACC): Cruise control system for road vehicles, automatically adjusts the vehicle speed to maintain a safe distance from vehicles ahead.
3) Lane departure warning system and Lane Change Assistance
4) Blind Spot Information System
5) Collision avoidance system
6) Intelligent speed adaptation (ISA): Constantly monitors vehicle speed and the local speed limit on a road and implements an action when the vehicle is detected to be exceeding the speed limit.
7) Night Vision & Pedestrian protection system
8) Traffic sign recognition
9) Hill descent control System.
Some more commercially available systems are:
Speed Adviser: ISA (Intelligent Speed Adviser) smartphone app
Speed Adviser is a smartphone app designed to reduce speeding and save lives. First released in February 2014, Speed Adviser provides free access to accurate speed zone information and warnings across the road network. The Speed Adviser ISA smartphone app is designed to reduce speeding and save lives.
Community Speed Watch
Vehicles being driven too fast are a major factor in preventing people enjoying of the environment in which they choose to live. Excess vehicle speed also contributes to the severity of any road traffic collision and has an impact on the lives of people within a community. Community Speed Watch is a traffic monitoring scheme co-ordinated by the police and the Local Authority. The aim is to help local people address speeding problems in their community.
Honda’s zero collisions scenario
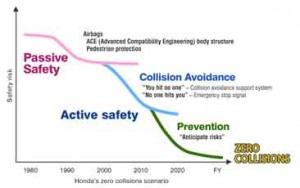 In April 2013, Honda adopted “Safety for Everyone” as its global safety slogan in order to further the Honda Environmental and Safety Vision comprised of “Realizing the joy and freedom of mobility and a sustainable society where people can enjoy life.” To achieve collision-free mobile society, Honda has devised what Honda called “collision-free scenario.” To do this Honda combine a “passive safety” component (air bags, pedestrian test dummies, etc.) and an “active safety” component (technology to avoid hitting or being hit by other vehicles), and popularize these with as many as customers can be done.
In April 2013, Honda adopted “Safety for Everyone” as its global safety slogan in order to further the Honda Environmental and Safety Vision comprised of “Realizing the joy and freedom of mobility and a sustainable society where people can enjoy life.” To achieve collision-free mobile society, Honda has devised what Honda called “collision-free scenario.” To do this Honda combine a “passive safety” component (air bags, pedestrian test dummies, etc.) and an “active safety” component (technology to avoid hitting or being hit by other vehicles), and popularize these with as many as customers can be done.
ICT key to improved road safety – Ericsson
We all often listen road campaigns’ like “Don’t text and drive”, Use hand-free devices, Don’t talk on mobile while driving and many more. And the concern is quite valid when we know that 70% of serious road accidents are caused by distracted drivers. But ICT (Information & Communication Technology) offers just as many opportunities to make driving safer. Take for example Project Cooperative Cars (CoCar), where Ericsson and other telecom players have teamed with the automotive industry, under the auspices of the German Government, to find innovative ways to use car-to-car (C2C) and car-to-infrastructure (C2I) communication. Among other findings, CoCarX (CoCar Extended) determined that LTE networks provide sufficient bandwidth, and therefore speed, to provide time-critical driver assistance.
eCall – emergency Calling – Initiative by European Union
The European Union is going to have eCall installed in all vehicles by 2015. eCall is an automated system that connects immediately to emergency services when a vehicle is involved in a serious accident. So even if the driver is unconscious, help will be dispatched to the exact location. This immediate notification and precise coordinates have proven to cut response times by 50 percent in rural areas and 40 percent in urban ones. These crucial minutes can be the difference between life and death, a short hospital stay and permanent injury. Ericsson is one of the partners working on the Harmonized eCall European Project (HeERO) to implement a standard eCall solution across the EU.
Augmented Reality Dashboards – Under Development
For cars equipped with GPS systems, Augmented Reality dashboards, AR for short, are the next window. The basic concept is the system looks at a person or an object and automatically brings up information about them and can identify who or what they are, what the distance & speed is and may could raise alarm or take self initiative. BMW are developing augmented reality dashboards that will be able to identify objects in front a vehicle and tell the driver how far they are away from the object. The AR display will overlay information on top of what a driver is seeing in real life. An augmented reality GPS system could highlight the actual lane you need to be in and show you where you need to turn down the road without you ever having to take your eyes off the road.
Driver Drowsiness Detection in Tata Elxsi
Monotonous driving, e.g. on expressways, is exhausting and quickly leads to loss of concentration. Based on steering-angle data, the function Driver Drowsiness Detection continuously analyzes the steering behaviour of the driver to identify phases during which the driver does not steer for a brief period and then makes an abrupt correction – often a sign of failing concentration and arising tiredness. As well as warning the driver, data concerning the tiredness of the driver can be used by other systems in the vehicle. Tata Elxsi developed an algorithm for Driver Drowsiness detection. Tata Elxsi was involved in integrating the driver drowsiness detection algorithm with the seat system, wherein the system will be triggered by the signal pulse from the drowsiness detection system.
Predictive Emergency Braking System launched in Mercedes Benz S Class
A brief distraction or loss of concentration can often be sufficient to cause a rear-end collision. Accident research shows that prior to rear-end crashes most drivers do not apply the brake pedal strongly enough, or do not apply the brakes at all. For these reasons Bosch has developed the Predictive Emergency Braking System. It assists in avoiding rear-end collisions and mitigating the consequences. In Mercedeas Benz S class, introduced an Adaptive Brake with Hold mechanism. The HOLD function of the ADAPTIVE BRAKE System is activated by firmly depressing the brake pedal, preventing the vehicle from rolling unintentionally at lights or in stop-and-go traffic.
ESC – Electronic Stabilisation Control by Volksvagen
Advanced Electronic Stabilisation Control from Volksvagen detects critical situations to stop skidding before it begins. ESC predicts what your car is about to do. It uses sensors to monitor the progress of your wheels and the moment they start to slip, ESC takes over by:
- Applying the brakes to one or more wheels
- Reducing engine power if necessary
- This fast, effective reaction stops skidding before it begins.
Volvo Claims Road Magnets are Safer than Cameras and GPS Systems for Self-Driving Cars
Future autonomous self-driving cars are set to rely heavily on GPS systems and cameras to drive on the road without intervention from a driver. But Volvo claims that the GPS systems and cameras have limitations in certain conditions and is now testing road magnets as a more reliable and safer method to guide self-driving cars down the road. Volvo teamed up with the Swedish Transport Administration to create a 100-meter long test track at its testing facilities in Hällered outside Gothenburg, Sweden. A pattern of round 40×15 mm ferrite magnets were placed 200 mm below the road surface and the car was equipped with several magnetic field sensors. The project was designed to evaluate crucial issues, such as detection range, reliability, durability, cost and the impact on road maintenance. “The magnets create an invisible ‘railway’ that literally paves the way for a positioning inaccuracy of less than one decimeter.
Renault Concept Car Launches Drone to Check for Gridlock Ahead
Renault has dreamed up a concept car that would include a “flying companion” in the form of a quadrocopter. The tiny drone would launch from a special compartment in the car’s roof. Should the concept every become reality, the drone could be controlled manually via a tablet or be set to fly autonomously to pre-determined GPS waypoints, presumably matching your driving speed. It would come in use by flying in front of the car to warn of dangers on the road ahead.
Self-Parking Cars
A new pilot project is being launched which will introduce us to self-driving and self-parking cars. The project called ‘Drive Me’, is being trailed in the Swedish city of Gothenburg, with 100 self-driving Volvos due to take to the roads. The scheme is aimed at reducing accidents and cutting down fuel consumption. Volvo’s Drive Me venture kicks off subsequent year, commencing with the development of client analysis and infrastructure technological innovation just before setting 25 self-driving automobiles loose on the streets of Gothenburg in 2017.
Vehicle communication systems
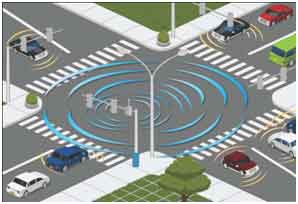 Vehicle Communication Systems are an emerging type of networks in which vehicles and roadside units are the communicating nodes; providing each other with information, such as safety warnings and traffic information. As a cooperative approach, vehicular communication systems can be more effective in avoiding accidents and traffic congestions than if each vehicle tries to solve these problems individually. The next level V2V system can be connected with a centralized road traffic system, that can raise alarm for diversions ahead of emergency vehicle ahead.
Vehicle Communication Systems are an emerging type of networks in which vehicles and roadside units are the communicating nodes; providing each other with information, such as safety warnings and traffic information. As a cooperative approach, vehicular communication systems can be more effective in avoiding accidents and traffic congestions than if each vehicle tries to solve these problems individually. The next level V2V system can be connected with a centralized road traffic system, that can raise alarm for diversions ahead of emergency vehicle ahead.
Challenges for Indian Roads
1. Technological up gradations in a vehicle will add to its cost
The reality check seems different than it is. Anyone can pay more money for more comfort or status, but for security features, In Indian market definitely no for 80% of users, especially low end vehicles owners. Definitely a smart & equipped car will cost much high and May not be acceptable by mid-low end car manufacturers & owners. This factors has to be considered by govt. to provide aids to manufacturers for these types of technologies and bought them in reach of conman man.
2. Internet connections
For cars to be intelligent they have to be connected with a Wi-Fi cloud network that may not be available in rural or remote areas or extreme whether cases. So a backup human interface is a musty for every aspect of intelligent Cars.
3. Making it legal
Various laws will have to be updated around the country to make it legal for automated cars to drive on the road. Insurance and liability are particular tricky. If a car driving itself gets into an accident that result in damages or injuries, who is responsible? The driver or the manufacturer that designed the car. Researchers and makers of driverless cars say the technology will be far safer than people-driven vehicles because they eliminate unpredictable human errors like distracted or drunk driving, or poor reactions to emergency situations.
4. Will the public want them?
Suppose you are driving a Mercedes fully automated car on a high-way and suddenly a cow comes in front of you. For cow reacting on upcoming car or horn is quite difficult. Making it full responsibility of driver. In India apart from pedestrians & cyclist, animals can be easily seen roaming even on highways. Apart from this, Indian roads are really in pathetic conditions, full of pits and are non-uniform. Knowing all these things de-motivates car owners to go for costly security techniques. It may seem wasteful to them and government is required to make roads ready for world-class cars to came in India.
5. Privacy
Privacy will be another big concern. The various sensors and in-car systems can collect data about driving patterns and locations and save that data in the cloud. The idea is to use this information to assist the driver, say updating a car’s route based on real-time mapping information. And this data could be hacked and can be used dangerously by 3rd person and could serious accidents.
6. Illiterate drivers
In India, there is no provision of driver training or norms for minimum education level. Completely illiterate peoples do have licenses for commercial vehicles even. The more a car is smart the more it relies on its software & firmware. This adds trouble & fear factor to the driver hardly understood English language. This fact makes its very important to literate drivers about the hi-tech software and other operating media. In addition to this add an importance to connect these cars with a help centre for a call of emergency.






