The Raspberry Pi has been put to countless creative uses, with its low cost and easy to use GPIO, coupled with a passionate and inventive community, giving birth to applications that have ranged from simple fun, to inspired and even profound. However, the single-core Raspberry Pi i.e. former versions of Raspberry Pi couldn’t be everything to everyone due to somehow limited functionalities.
The Raspberry Pi 2 Model B, with its quad-core processor and 1GB RAM weighs assures around six times the performance of its predecessor and accommodates other applications far better. A great example being software-defined radio (SDR), where components usually implemented in hardware are instead implemented in software, resulting in flexibility, but at the cost of being computationally intensive.
Installing GNU Radio
 The GNU Radio SDR toolkit is a fairly substantial codebase and with some equally heavyweight dependencies. The new raspbian packages are based in “Jessie Testing Release”. The MicroSD card that come supplied with the Pi 2 is based on wheezy, but adding a line to the Apt configuration was all that was needed to get Jessie packages.
The GNU Radio SDR toolkit is a fairly substantial codebase and with some equally heavyweight dependencies. The new raspbian packages are based in “Jessie Testing Release”. The MicroSD card that come supplied with the Pi 2 is based on wheezy, but adding a line to the Apt configuration was all that was needed to get Jessie packages.
Coding
Edit /etc/apt/sources. list and add the line:
deb http://archive.raspbian.org/raspbian jessie main
Update the Apt cache:
$ sudo apt-get update
Install GNU Radio runtime and development files:
$ sudo apt-get install gnuradio gnuradio-dev
Setting up RTL-SDR
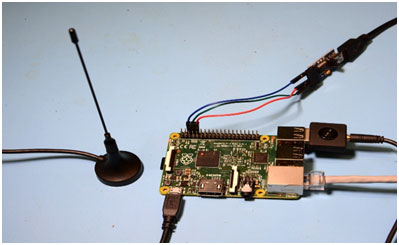 It is amazing to note that a USB TV tuner dongle plugged in to one of the USB ports of Raspberry Pi 2 and the supplied antenna attached.
It is amazing to note that a USB TV tuner dongle plugged in to one of the USB ports of Raspberry Pi 2 and the supplied antenna attached.
We are re-purposing a TV tuner that is supported by the Linux kernel and which would otherwise be claimed for TV reception, we need to first stop the kernel from doing so.
Coding
Edit the file /etc/modprobe.d/raspi-blacklist.conf and add the line:
blacklist dvb_usb_rtl28xxu
Install the rtl-sdr software and GNU Radio support:
$ sudo apt-get install rtl-sdr gr-osmosdr
In order to access the device as a non-root user we need to set up a new udev rule, but first we need to ascertain the USB ID. Ensure that the tuner is plugged in and type:
$ lusb
This gave me:
Bus 001 Device 004: ID 0bda:2832 Realtek Semiconductor Corp. RTL2832U DVB-T
Next we create the file /etc/udev/rules.d/20.rtlsdr.rules, with the line:
SUBSYSTEM==”usb”, ATTRS{idVendor}==”0bda”, ATTRS{idProduct}==”2832″, GROUP=”adm”, MODE=”0666″, SYMLINK+=”rtl_sdr”
A simple test
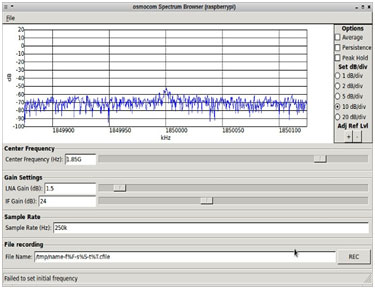 To get a simple spectrum display we can run the FFT application which is provided as part of the gr-osmocom software.
To get a simple spectrum display we can run the FFT application which is provided as part of the gr-osmocom software.
$ osmocom_fft
If we then check the CPU load we can see that we have plenty of capacity to spare, with just one core at around 70% utilization.
gr-air-modes
You can use rtl-sdr hardware together with the GNU Radio-based gr-air-modes software, to receive position and heading information from aircraft Mode-S transponders.
In order to build gr-air-modes a few additional dependencies are required.
$ sudo apt-get install sqlite pyqt4-dev-tools liblog4cpp5-dev swig
With these installed the sources can be cloned from GitHub:
$ git clone https://github.com/bistromath/gr-air-modes.git
To then build and install:
$ cd gr-air-modes
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake ../
$ make
$ sudo make install
$ sudo ldconfig
We can then run the application with:
$ modes_rx -s osmocom
Conclusion
The Pi 2 provides a marked improvement on the first generation hardware, with four cores instead of one and each of these being a more recent and more powerful version of the ARM architecture. There is significant improvement in performance that will be welcomed by many and not least of all those with SDR applications in mind.
About RS Components
RS Components is a high service distributor of electronics and maintenance products. We offer around 500,000 products, sourced from 2,500 leading suppliers; include electronics, automation and control, test and measurement, electrical and mechanical components.
For more information, please visit the website at www.rsindia.com
Reach out to us at: Tollfree: 1800 180 7746, Tel: + 91- 120- 4519100, fax: +91-120- 4519198/199
RS Components & Controls (I) Ltd
B-74 Sec 60, Noida 201301.
For more information, please visit the website at www.rsindia.com
Reach out to us at – sales@rs-components.co.in






