
Mr. Krishnan Shrinivasan, Vice President and Managing Director, Lam Research India
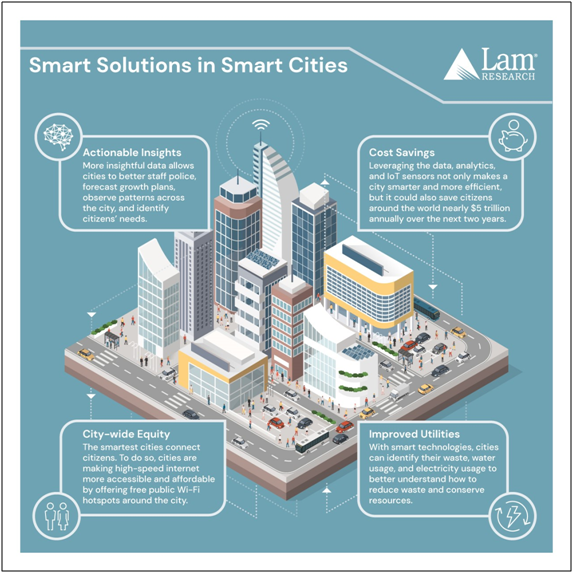
Cities around the globe are experiencing software updates – swapping out antiquated data collection techniques for new technological initiatives to promote efficiency, transparency, and sustainability. The introduction of real-time analytics is ushering in the newest wave of smart cities in history. The combination of cloud-based dashboards and machine learning developed on top of chip technology is providing actionable data to be collected and used to improve cities.
The progress achieved through smart cities has inspired municipal governments to leverage smart technology to improve infrastructure, efficiency, and overall quality of life. Let’s look at these advancements.
What Are Smart Cities?
A smart city is a connected community that incorporates Internet of things (IoT) technology to deliver the highest quality living experience – promoting economic stability, mobility, and sustainability. The advanced technology provides useful insights to better allocate resources to improve city operations, as well as the quality of life for citizens and visitors. For example, semiconductor-enabled cameras can capture high resolution real-time footage of the city, allowing city officials to monitor the flow of traffic, pedestrian walkability, street safety, and construction.
Due to the rapid urbanization of cities, governments have relied heavily on advanced technology to accommodate the flash growth. Early reports indicate that roughly 68% of the population is expected to live in cities by 2050, which equates to 2.5 billion people. Smart cities offer a tangible and cost-effective way to make growing cities more efficient, while ensuring citizen safety. As cities become smarter, they are far better equipped to manage the influx of people.
Benefits and Applications
The advanced analytics gathered from IoT and machine learning technologies provide a deeper analysis of ongoing pedestrian activity to optimize city planning and operations, understand emerging neighborhoods, and improve city safety and walkability. Connected mobile apps can now provide immediate access to city data, open parking spaces, or for citizens, a method by which to report failing infrastructure.
The new digital services make cities more attractive for people and businesses, and fosters communication between the citizens and local government. The improved communication ensures more civic engagement and can build trust among city officials. With real-time access to activities in the city, citizens have more access to government data and can even attend live-streamed city hall meetings. Smart cities also have made vast improvements in their carbon footprints, as well. Smart cities benefit the environment with energy-efficient buildings, air-quality sensors, and renewable energy resources to address high pollution areas.
Smart City Examples
As the benefits of advanced technologies have become more apparent, the number of cities implementing such technologies to become smarter have skyrocketed. Although the earliest adopters of smart city technology were European governments, U.S. cities have quickly followed. Now, we’re approaching 300 smart city projects worldwide. Below, are a few noteworthy examples.
• San Francisco, USA: San Francisco city officials identified that more than half of all trips in San Francisco used public transit. As a result, the city invested $11 million to implement projects to reduce travel time, traffic congestion, and traffic crashes. The plan aims to reduce vehicle transit and transportation emissions by 10% through electrification. In addition, the newly minted SFpark project uses wireless sensors to create smarter parking management. The sensors send app-users the closest available parking spot. SFpark has helped reduce traffic miles and greenhouse gas emissions by 30% in pilot areas.
• Grenoble, France: France is expanding its public transportation network in a move toward multi-modality. The city of Grenoble rolled out its new transportation initiative, Cité lib by Ha:mo, which introduced 70 all-electric, ultra-compact vehicles to be used for short city trips. Along with the electric vehicles, the city installed 27 charging stations. The electric vehicles give Grenoble citizens and tourists new green options for commuting.
• Osaka, Japan: Asia is also making significant strides toward smarter cities. The Osaka, Japan, which houses nearly 3 million citizens, is placing a premium on smarter homes and recycling initiatives. Osaka is also focusing on promoting global warming awareness and reducing emissions. The city uses advanced technology to continuously monitor air pollutants and offers direct feedback to citizens. Additionally, Osaka’s City Council has piloted the Smart Home project, which offers citizens a clean home energy solution. The program has already resulted in an 88% reduction in energy use.
Leveraging advanced technologies has played a major role in cities identifying high-risk areas, planning for expansion, and identifying trends. With so many people migrating to urban areas, it is important for local governments to find ways to use innovative technologies to accommodate the rapid growth. As chip technology continues to improve, cities will have more tools at their disposal to make their cities smarter.






