Authors:
- Alok Kumar Mittal – Group Manager, SRA (System Research and Applications), India, STMicroelectronics
- Kamaldeep Bansal – Staff Engineer, SRA (System Research and Applications), India, STMicroelectronics
Introduction
Electronics is every-where now. The electronics based systems usage has exploded exponentially and has entered all aspects of our life weather it is automotive, white goods, entertainment, wearables and what not! This has happened due to large integration of electronic devices to make very complex and computational intensive micro-controllers and SOCs (systems on chip). Today consumer whitegoods and electronic designs are getting complex day by day which is bringingthe focus of designers to ease of usage and troubleshooting.
The complexity of design requires greater need for the internal debug information to understand what is happening inside the computing unit and if there are faults or failures seen,it can be retrieved and checked at various stages of product life cycle as shown below.
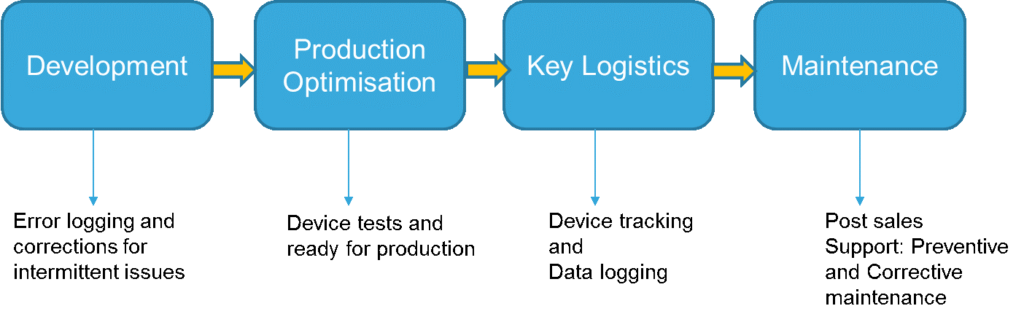
Product development and engineering:
For embedded systems, it may be needed to observe and certify the reliability of the product by checking the performance over long period of time. Manually observing the behavior of the system may not be feasible or efficient. It can be challenging as well to analyze big data and need specific analysis.
The intermittent failures or conditional failures can only be debugged after the right logging of events and errors cases. This information is already available and checks are already put in place by the developer. Providing these information externally for analysis requires a small amount of memory or dumping of the internal information
Product manufacturing:
These self-tests and error codes or messages are helpful in quality assurance during product development and manufacturing, optimization of test time and production tests and even post-sales maintenance.
If there is an error, the system already provides the information on which part was not able to communicate well and hence caused the problem. This can be tested or debugged by a technician easily and repairs can be carried out.
Logistics logging:
Some key products may require specific mode of transport and logistics. These kind of systems may keep track of environmental and handling electronic data into the internal memory like shock, humidity and temperature.
These data can be analyzed at destination to check if the product moved in recommended mode of transport and handling
In field service:
The user can use the smart-phone to retrieve the internal information of the product installed in field. This information is very useful for the maintenance service provider and can help the company to inform the staff to be rightly prepared for the service call. This not only save the number of visits for the maintenance but also the time in the service call.
Currently used methods for debugging the systems
While, the LEDs, LED segments and LCDs have limited capability to provide error information, the new smart connectivity can provide much more information to the user. These open new way of capturing information, debugging, production level quality check and optimization of test time and post-sales maintenance.
New smart connectivity methodfor debugging using NFC
Most of the embedded systems have internal non-volatile memory for the storage of some system parameters. When this EEPROM is replaced by a Dual-Interface EEPROM, it can further be used for the error reading and system health using wireless communication
The active RFID tags can provide very cost effective error codes logging. These can be retrieved by a NFC interface.
NFC (Near Field Communication) is a wireless technology based on RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) at 13.56 MHz that establishes a communication between the devices by bringing them in close proximity. Today most of the mobile phones have NFC interface. This can be used to communicate with Active tags to the information exchange with user.
System Architecture
Consider that in a system, like a consumer product, an active tag can be very useful for the self-diagnosis. When the system is powered ON, all parts of the systems are checked and the status is written in the already available Active-tag. This can be read during final quality check and if all the parameters are found to be ok, the product is shipped.
Testing all parts of the system in one step can also save time during the production line. It takes few seconds of time to read the system health. A smart-phone or a reader can show the meaning of the error by suitable apps and it can be a very easy user interface.
While, if there is an error, the system already provides the information on which part was not able to communicate well and hence caused the problem. This can be tested or debugged by a technician easily and repairs can be carried out.
This method can also be used in post-sales. The user can just touch the smart-phone on the panel of the white good and read the internal information via NFC. This information can be sent to the central servers while logging the complaint automatically via WAN connectivity like Wi-Fi or GPRS connection.
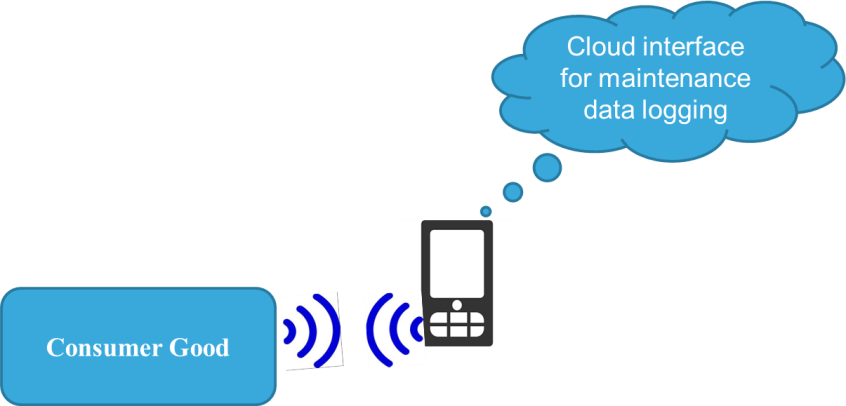
Implementing NFC based smart connectivity for easy debugging
Microcontroller controlled embedded system can test its internal logics and external peripherals connected with it. Self-test report can be updated on smart phones using NFC. Some testing commands can be given using phone to further analyze the problem.
NFC connectivity is a very cost effective, compact and noise free solution which can be incorporated easily even in small systems
Today mostly people have smart phones which can be used to test system and then to give its preliminary information along with the type of fault which can be displayed on phone using android application. For better understanding pedometer system has been taken as example. Below is the block diagram of pedometer system:
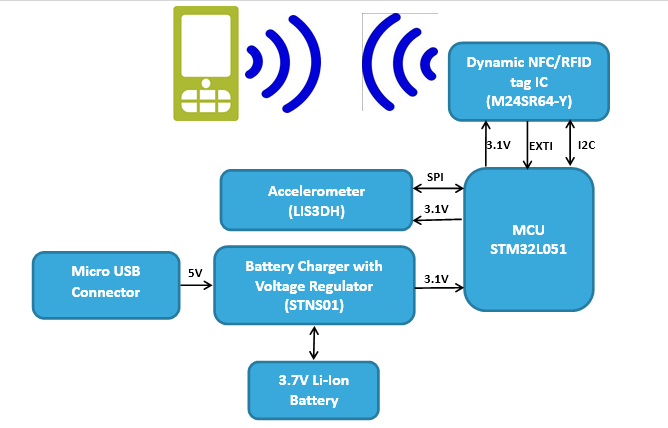
Wearable Pedometer is implemented using STM32L seriesmicrocontroller which reduces the power requirement for concerned application & provides adequate processing capabilities ideal for this application. It also has various on chip peripherals like SPI, I2Cand ADCwhich helped in designing low cost and low power solution.
Dynamic NFC/RFIDtag IC M24SR64-Y has the capability to operate from an I2Cinterface or by a 13.56 MHz RFID reader or an NFC phone. It helps in establishing low cost RF Communication between pedometer and phone. It embeds anEEPROM memory which is used to save the system status and other required information.

To take the advantage of troubleshooting sytem without opening the system, An Android app has been developed which can communicate with the system without making physical contact. Even Dynamic NFC/RFID tag IC does not require the power supply to communicate using RFID reader. To check the status of the system, phone has to bring near to the system to initiate the communication.

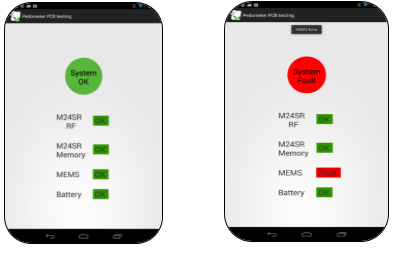
Dynamic NFC/RFID tag IC has a pin which can be configured to generate an interrupt for the main controller to wake up the system with the presence of NFC. With the interrupt system can run configured tasks to check the system health & write the status in NFC IC. Then NFC can be read using RF link to check system status. Eventually phone displays the system status like “System Ok” pops up to tell that overall system is ok. Otherwise “System Fault” pops up in case of faulty systems mentioning the area in which fault has occurred.
Conclusion
Smart connectivity in systems can give multiple benefits starting from the production to the servicing in hand of customer. This can help reducing the overall costing of the product. Out of the smart connectivity options available today, NFC could be a good choice as it is economical, require very low power & space which makes it ideal for any of the application weather small or big.






