Sabrina Bochen, Senior Principal, Cellular Product Strategy, u-blox
Smart city trial programmes are becoming ubiquitous globally, and the connectivity infrastructure is aligning with low power wide area (LPWA) technologies to enable applications including smart buildings, smart street lighting and smart metering. India has already announced an extensive smart city program, and LPWAN will power the connectivity for the IoT in these deployments.
The urban environment in India is characterized by a continuous and ultra-high-density flow of populationwhich, in turn, creates unique challenges for mass connectivity to underpin these smart city initiatives.Emerging narrowband cellular standards offer features that suit the challenges of connecting nodes in India’s dense metropolitan networks.
Smart Cities Mission in India and IHS Analysis
In June 2015, the Indian government’s Ministry for Housing and Urban Affairs launched Smartnet, the Smart Cities Mission and Challenge, to expand smart cities in India. The Smart Cities Mission’s aim is to drive economic growth, creating 100 smart cities, improving citizens’ quality of life, creating a clean and sustainable environment, upgrading and deploying new infrastructure, and setting examples to be replicated by other cities. The Mission has been planned to last for five years, running from full year 2015–16 to 2019–20. After this timeframe, the Mission could be continued and adapted in light of the results and lessons learned during this period. To assign the available funds, cities participate in a contest called Smart City Challenge.
Each city participating in the contest presents a proposal including a pan-city initiative (i.e. a solution applied to the whole city) and area-based developments in the form of retrofitting, redevelopment or greenfield projects. The need to present both area-based and city-wide initiatives was established to ensure that the whole city population could benefit from the creation of smart city projects.
The Smart Cities Mission and Challenge does not specify the type of solution to be proposed by the city,and these can include solutions in the energy and efficiency sector such as smart water meters, or in the safety and security sector such as intelligent video-surveillance systems. While drafting the proposal, each city should account for its local characteristics and needs.
The central government will invest a total of INR48,000 crore (USD7.4 billion) over the next five years, an average of INR100 crore per city per year. Funding will also come from the state and the urban local bodies (ULB). The first year, winning cities will receive a larger sum, of INR200 crore, to be better equipped to start the projects. The aim of the government fund is not to fully sustain the cost of all the projects, but to jump-start the smart city market and act as a catalyst, attracting further investments.
India Unveils 30 More Winners of the Smart City Challenge
Earlier this year, India selected 30 cities in the third round of the Smart Cities Mission national program.With this announcement, India has now selected 90 cities to date, with total investment for the 90 cities reaching INR191,155 crore (USD 29.6 billion).
In this round of selection a total of 45 cities competed for 40 available opportunities. However, only 30 cities were selected to ensure feasible and workable plans. As part of the Mission the government will provide INR500crore (USD77.4 million) to each of the winning cities for a five-year period.
Networks for the Smart City and Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT)
The emerging NB-IoT technology promises to deliver a more affordable and power-efficient way to connect small, battery-operated remote devices to the Internet.This positions the technology as a strong fit for making municipal applications like utility metering, street lighting, smart parking and toll road charges more efficient and effective.
Backed by the NB-IoT Forum, a group led by major carriers and equipment vendors like Vodafone, Nokia, Ericsson and Intel, NB-IoT is one of three newly released cellular narrowband standards from the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), which develops telecommunications standards.
Smart Cities’ Need for Better IoT Solutions
“Reducing cost and power consumption while increasing coverage are the main drivers,” explains Simon Glassman, senior principal of strategic partnerships in Europe, the Middle East and Asia for u-blox, a member of the NB-IoT Forum. “There is a wide range of IoT application areas where mass adoption is held back by the inability to meet one or more of these requirements.”When there is coverage, it is often poor or unable to cope with a high volume of connections and requires the device transmitter to operate at high power, draining the battery.Cellular networks are not optimized for applications that only transmit small amounts of infrequent data.
Enter NB-IoT, which offers a platform “for ultra-low-cost, low-throughput use,” Glassman says. “The standard coexists with LTE and can be deployed in bands using resource blocks within normal LTE carriers, or stand-alone for deployments in a dedicated spectrum.”
With NB-IoT, municipalities could bring small battery-powered devices like utility meters online, and those devices won’t need recharging for a decade.Local governments could use devices connected via NB-IoT to control lighting, check when trash cans need emptying, identify free parking spaces, monitor environmental conditions and more.
Partnership Targets Local Infrastructure Providers to Deliver Rapid Development of IoT Connectivity
In August, u-blox, a global leader in wireless and positioning modules and chips, and Bangalore-based Atoll Solutions Pvt, a leading IoT gateway platform, sensor node and wireless module provider, announced the availability of an IoT starter kit based on LTE Cat M1 and narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) modules from u-blox.
With India’s smart city program gaining pace and traction, the communications infrastructure to support it is moving toward LPWA technologies to enable smart street lighting, smart metering and other applications. The starter kit provided by this alliance makes an ideal development platform for nodes and gateways based on both LTE Cat M1 and NB-IoT.
Supporting both the NB-IoT (LTE Cat NB1) SARA-N2 and LTE Cat M1/NB1 SARA-R4 module series from u-blox, the starter kit will enable local infrastructure providers to rapidly develop IoT solutions, ready for deployment in a smart grid.Future development will include complete reference designs incorporating other u-blox solutions, including Bluetooth Low Energy and GNSS modules.
The u-blox SARA-N2 series are the world’s first power-optimized NB-IoT (LTE Cat NB1) modules.Measuring just 16.0 x 26.0 x 2.4 mm they provide ultra-low power consumption, delivering 10+ years of battery life.Other features include excellent extended range in buildings, including underground, with a maximum coupling loss of 164 dB.The very small SARA LGA form factor also makes for easy manufacturing.
The u-blox SARA-R4 series are ultra-compact LTE Cat M1/NB1 modules.Measuring just 16.0 x 26.0 x 2.5 mm, they provide global configurability with a single hardware version.They also offer the flexibility to select M1 only/preferred or NB1 only/preferred modes.The low power consumption extends battery life, and coverage enhancement gives extended range in buildings and basements and, with NB1, underground too.
Both families provide easy migration between other u-blox cellular connectivity modules and an extended temperature range of -40 to +85°C, very useful for the hot conditions inside street cabinets in Indian cities.
The u-blox modules are further supported by the C030 Mbed-enabled IoT starter kit, the EVK-N2 SARA-N2 series cellular evaluation kit and the EVK-S4 SARA-R4 series cellular evaluation kit,which are powerful and easy-to-use tools that simplify the evaluation of u-blox SARA-N2 and SARA-R4 series LTE Cat M1 and NB-IoT modules.In addition, the m-center cellular evaluation software for Windows is a powerful and easy-to-use tool for evaluating, configuring and testing of u-blox cellular modules. It includes an intuitive, easy-to-understand and easy-to-use graphical interface. m-center is available free of charge.
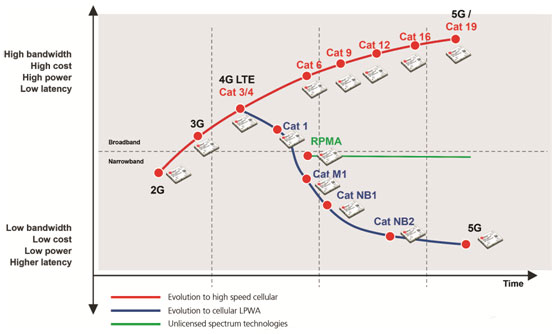
Figure 1 shows the roadmap for LTE and the path taken by a sub-group of LPWA technologies, such as narrowband-IoT/Cat NB1, aimed at a broad range of low power, low data rate applications – i.e. ideal for smart city connectivity.
“Many leading cellular operators in India are already offering LTE Cat M1 and NB-IoT support, with many more about to follow,” said Rado Sustersic, Product Manager, Product Center Cellular at u-blox. “This announcement will help accelerate the adoption of lowpower widearea (LPWA) technologies for smart cities and provide OEMs with the tools they need to get to market quickly.”
“Narrowband LTE has the power to add affordable and reliable connectivity to a wide range of assets, creating truly smart cities through smart lighting and smart metering,” commented Jithu Niruthambath, Founder and CEO of Atoll Solutions Pvt. “We believe this starter kit will enable our customers to build and deploy scalable solutions in the IoT with ease and confidence.”
Atoll Solutions offers IoT gateway platforms, sensor nodes and wireless modules that customers can use to build optimized and ready to deploy IoT solutions in industrial, remote monitoring, logistics and automation applications.Atoll Solutions has partnered with industry leaders like u-blox to bring IoT technologies and building blocks to their gateway solutions, allowing OEMs and system integrators to build and scale solutions quickly, easily and securely.






