
Fiber optic sensing systems assist critical infrastructure ranging from telecommunication services, oil, gas and water pipelines to mining, marine applications, electrical power transmission and data center interconnects in optimizing efficiency and implementing preventive protection and security. Fiber sensing technology involves the integration of optical fibers within the infrastructure to monitor various physical parameters in real time that can prevent outages, avoid costly repairs to critical infrastructure and help in faster restoration.
Fiber optic sensing
Fiber optic sensing uses the physical properties of light as it travels along a fiber to detect changes in temperature, strain, vibration (acoustics) and other parameters. Fiber optic sensing utilizes fiber as the sensor to create thousands of continuous sensing points along the fiber. The technique is called “distributed fiber optic sensing,” where a standard single optical fiber can act as an extended sensor over long distances and with high spatial resolution, covering vast areas of critical infrastructure.
Changes in the surrounding physical parameters, such as strain or temperature, cause minute variations in the light’s characteristics, which can be detected and analysed. Advanced signal processing techniques allow engineers to convert these variations into valuable data. Traditional fault detection methods can be slow and costly, often requiring extensive manual inspection. Fiber optic sensing can quickly identify and locate faults caused by physical damage, environmental factors or operational anomalies.
Applications of fiber optic sensing
Distributed fiber sensing offers a versatile range of capabilities, enabling monitoring of various physical parameters critical to infrastructure health. The three primary types of fiber sensing utilized in infrastructure monitoring are for temperature, strain, and acoustics.
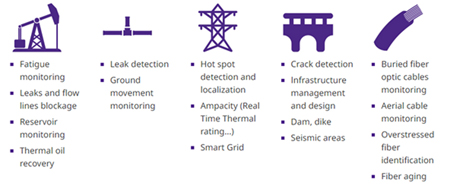
Temperature sensing: Temperature anomalies and overheating can significantly impact the structural integrity of infrastructures like; pipelines, electrical power cables, and electrical equipments. Distributed temperature sensing (DTS) utilizes the principle of measuring the change in back-scattered light frequency or power as a function of temperature. This method allows for continuous monitoring of temperature profiles along the entire length of the optical fiber, providing valuable data on potential hotspots or temperature variations that might affect the infrastructure’s performance.
Strain sensing: Monitoring strain due to mechanical loads is crucial in assessing the health of civil engineering assets. Distributed strain sensing (DSS) relies on the principle of measuring minute variations in light frequency caused by mechanical strain applied to the optical fiber. This technique allows engineers to detect deformations, cracks, or excessive loads, helping prevent catastrophic failures and extending the lifespan of critical structures.
Acoustic sensing: Distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) is a cutting-edge technology that enables the detection and localization of acoustic disturbances and vibrations. By analysing changes in light scattering caused by mechanical pressure waves, DAS turns an optical fiber into an array of thousands of virtual microphones distributed over a vast area. This capability is particularly beneficial for monitoring large infrastructure networks, such as pipelines or railroads, as it can detect potential leaks, third-party intrusions, and interference, or even ground movements caused by seismic events.
The combination of these different types of fiber sensing not only provides a comprehensive solution for infrastructure monitoring but also opens up new possibilities for integrated and intelligent systems that can adapt to the evolving needs of complex and interconnected modern world. By harnessing the power of fiber sensing technology, organizations can enhance the safety, efficiency and reliability of critical infrastructure, ensuring a sustainable and resilient future.
Advantages of fiber optic sensing
Cost effectiveness: Traditional monitoring systems often require multiple sensors at various points, leading to higher installation and maintenance costs. Distributed fiber sensing, on the other hand, uses a single optical fiber to cover large areas, significantly reducing cost of deployment and operation.
Proactive maintenance: Distributed fiber sensing provides timely information on any changes or abnormalities, allowing for early responses to potential issues or threats.
Longevity and durability: Optical fibers and cables used in sensing are highly robust and can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for long-term infrastructure monitoring.
Remote sensing: Fiber sensing allows for remote monitoring, reducing the need for physical inspections and minimizing human exposure to hazardous locations.
Scalability: The technology is scalable and can be adapted to monitor various parameters simultaneously, providing a comprehensive monitoring solution for complex infrastructure systems.
NITRO fiber sensing
NITRO fiber sensing is an integrated real-time asset monitoring and analytics solution for critical infrastructure. Comprising Distributed temperature sensing (DTS), Distributed temperature and strain sensing (DTSS) and Distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) technologies, NITRO fiber sensing provides the critical intelligence needed to swiftly identify and locate threats.
Using remote Fiber test heads (FTH), commonly known as interrogators to monitor fiber optic cables or fiber-enabled infrastructure, NITRO fiber sensing measures temperature and strain along a fiber or detect acoustic vibrations close to a fiber in real time. NITRO fiber sensing offers solutions for industries like:
Power Transmission – real-time thermal rating (RTTR) and cable temperature, cable exposure and depth of burial and third-party interference.
Pipeline Infrastructure – real-time asset monitoring, leak detection and localization, and third-party interference detection.
Telecoms Infrastructure – cable health monitoring, smart cities and environment, plus detection of third-party interference with DCI.
Protection & Security – real-time perimeter monitoring, people and vehicle, tunnelling and excavation detection.
Ensuring safety and integrity of critical infrastructure
The continuous development and integration of fiber sensing technology into infrastructure monitoring practices will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in safeguarding critical infrastructure, providing engineers with the necessary tools to address challenges proactively and make informed decisions. As society becomes more connected, the demand for monitoring, security, and minimized reaction times will continue to grow. Creative utilization of fiber optic sensing will help make this possible.






