
Monojit Samaddar, Country Director, VIAVI Solutions, India
RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) enables the optimization of RAN resources through near real-time analytic processing and provides adaption recommendations. RIC is an open platform designed to host RAN control applications (called xApps) developed by specialist software developers – sometimes external to the RIC vendor.RIC helps operators to optimize and launch new services by allowing them to make the most of network resources, while helping operators ease network congestion.
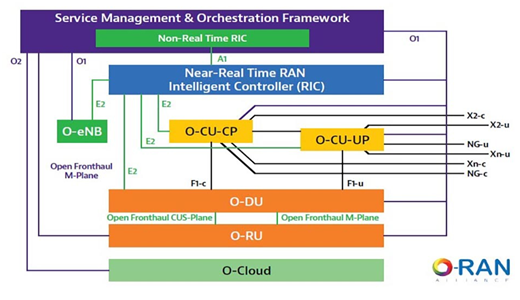
An O-RAN Alliance defined network component that aligns with 3GPP Release 15 and beyond the RAN Intelligent Controller is cloud native, and a central component of an open and virtualized RAN network. There are two types of RIC – a non-real time and a near real time – the main difference between them is the response time they take to effect changes in the RAN. The nRT RIC will turnaround decisions between 10 ms and 1 sec. While the Non-RT RIC feeds data collected from RAN elements into Near-RT RIC and provides element management and reporting. By keeping the RIC open and standard interface fosters innovation and time to market.
RIC enables interoperability across different hardware (O-RU, servers) and software (O-DU/O-CU) components in an O-RAN architecture. It features a standardized interface – called the E2 – from the O-CU and O-DU to the RIC. It’s along that interface that the RIC receives measurements from the RAN about the performance of the network.RIC then makes intelligent decisions to improve things like subscriber positioning, handover to a cell, and changing to different frequency. It adapts any variables in order to optimize the subscriber experience and network performance. To affect these improvements, intelligence is then sent back across the interface to the RAN and a measurement is then made to see if there’s been an improvement.
Objectives of the RIC
• Performance data – RIC receives a stream of RAN data (counters, KPIs, measurements) which can be analyzed by xApps and AI/ML engines to make RAN optimization decisions.
• Resource assurance – Ensure services attain required performance – using handover, modulation changes, prioritisation of RAN resources.
• RAN balance and harmony – Ensure RAN efficiency when many users are battling for scarce resources.
Challenges in deploying the RIC – Test is vital for success
• Complexity of deployment – A new element, new interface, new applications, new vendors, the RIC has a very important job of managing the RAN. For example; will 1 xApp undo another xApp, will outcome of 1 xApp invoke a reverse action by another xApp?
• Technology immaturity – The standards are still being defined. There will be new start-up companies joining the ecosystem; many may lack mobile communications experience.
• Integration with legacy systems – The RIC needs to work across different generations of mobile with 3G, 4G and 5G traffic mixed in a cell.
The Solution
RIC will become a key differentiator for mobile network operators to attract new customers, by showing how their network is out-performing the competition with real statistics. As with any new network element, testing is the only way to mitigate risk prior to deployment. TeraVM,a virtualized test tool that ramps up quickly and can change inputs at ease is enabling operators to test the RIC and in doing so is helping to expedite the roll-out of Open RAN networks and architectures. It can provide the emulated RAN (the measurements) to the RIC under test and then receive the outputs/decisions from the RIC and modify according to the proposed changes from the RIC. This makes it easy to see if changes improve the RAN efficiency. Extending its capabilities is just one way of supporting the evolution of networks and working with operators, to ensure easy, cost-effective ways of testing and readying their networks for their subscribers.






