India included broad development goals for its citizens, inclusive of improvement in the living standards in its two past five year development plans. Access to electricity plays an important role in enhancing the living conditions providing access to various interrelated measures refining the quality of life – productivity, health, safety, services etc. However the energy consumption pattern of India is majorly characterized by rural population, accounting to all most 71% of the country’s total population (source- Census 2011), lacking access to grid connected electricity supply, forcing the population to still depend on kerosene and candles for lighting purposes. These communities lack access to basic needs such as education, employment generation and are even exposed to greater health risk due to unclean lighting alternatives like candles, kerosene based lighting systems, etc. The vulnerable effects of these communities ask for a sincere need to provide clean, sustainable and affordable lighting solutions. This scenario is set to change with the introduction of off-grid lighting, catering to the needs of the people for lighting purpose. Lighting through off-grid means has emerged as a viable, user friendly and economical option for enhancing access to electricity in rural India.
India included broad development goals for its citizens, inclusive of improvement in the living standards in its two past five year development plans. Access to electricity plays an important role in enhancing the living conditions providing access to various interrelated measures refining the quality of life – productivity, health, safety, services etc. However the energy consumption pattern of India is majorly characterized by rural population, accounting to all most 71% of the country’s total population (source- Census 2011), lacking access to grid connected electricity supply, forcing the population to still depend on kerosene and candles for lighting purposes. These communities lack access to basic needs such as education, employment generation and are even exposed to greater health risk due to unclean lighting alternatives like candles, kerosene based lighting systems, etc. The vulnerable effects of these communities ask for a sincere need to provide clean, sustainable and affordable lighting solutions. This scenario is set to change with the introduction of off-grid lighting, catering to the needs of the people for lighting purpose. Lighting through off-grid means has emerged as a viable, user friendly and economical option for enhancing access to electricity in rural India.
Modern Off-grid lighting has emerged with the ascent to solar energy, battery and LED, providing an answer to the needs of these communities. The three basic components of off-grid lighting are as follows:
• Solar lantern.
• Solar home lighting System.
• Solar Street lighting system.
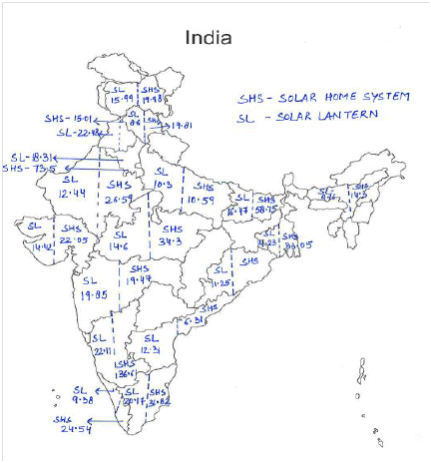
In India, solar lighting and solar home systems are the widely used forms of off grid lighting.. As per the latest reports of MNRE till now almost, .756 million solar lighting systems and, .62 million solar home systems have been deployed in the country . The figure depicts the percentage growth, dissemination of solar based off grid lighting systems in various states of India. On a cumulative basis on an average the growth percentage of solar lantern is accounted to be 14.83% and for solar home systems it is 27.78%
The Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission (JNSSM) set an ambitious target of installing 20 million solar home systems by 2022, lighting the lives of 100 million people in India. As per the UNEP’s research households earning USD 65 per month are subjected to the use of soalr lanterns and are not covered under the JNSSM scheme through which free solar home systems are distributed. Also as per the proposed cash transfer subsidy for keroscene in the 2010-11 budget, an estimated 50-55 million households enjoying the keroscene subsidy are likely to be excluded, thus resulting into the potential market for the solar home system and solar lanterns manufacturer’s.
The solar lantern market in India is characterized in both small and large enterprises, however the potential is still untapped. Multinational players such as Phillips and Schnider have recently entered the market of off grid lighting. The solar home system market in India comprised of already established players such as TATA BP solar, SELCO etc. TATA BP solar is the largest player in the market with the total market share of 25-30%.
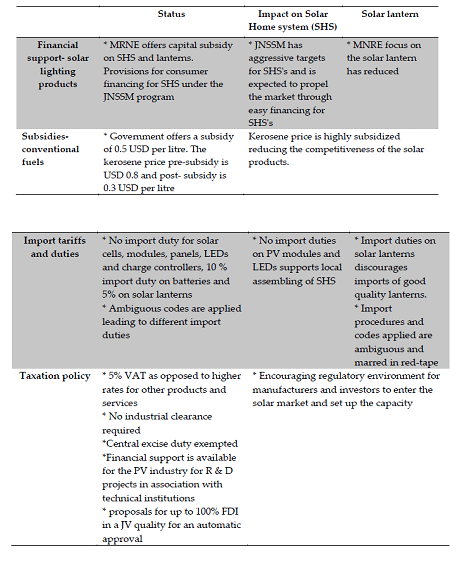
A wide range of LED, CFL based solar home system with varying panel wattage from 2.5 Wp to 75 Wp ranging from USD 40 to USD 50 respectively. Efforts are being made by a few companies to bring down the price of solar home systems to make it affordable to low income group. There’s been an annual growth of about 20-25% in the domestic production of solar panels , for about 1/3rd use in off grid lighting. The Government of India has also tapped the potential of solar and its contribution to energy for all The table below talks about the various measures taken up by the government to promote the off grid lighting.
 Solar energy has lately been realized as a form which could escalate the rate at which Indian economy is reaching up to its sustainable developmental goals. With about 21.3% of the population lacking access to electricity , India offers great potential for off grid lighting. Though various subsidy schemes, taxation policies, financial support have been provided by the Government of India, what is required at this stage is proper implementation of off grid lighting plans to achieve long term goals, which depends on effective prioritization, planning, appropriate infrastructure and sustainable financing, playing a key role in effective disposition and dissemination of this technology, striving towards sustainable future goals.
Solar energy has lately been realized as a form which could escalate the rate at which Indian economy is reaching up to its sustainable developmental goals. With about 21.3% of the population lacking access to electricity , India offers great potential for off grid lighting. Though various subsidy schemes, taxation policies, financial support have been provided by the Government of India, what is required at this stage is proper implementation of off grid lighting plans to achieve long term goals, which depends on effective prioritization, planning, appropriate infrastructure and sustainable financing, playing a key role in effective disposition and dissemination of this technology, striving towards sustainable future goals.