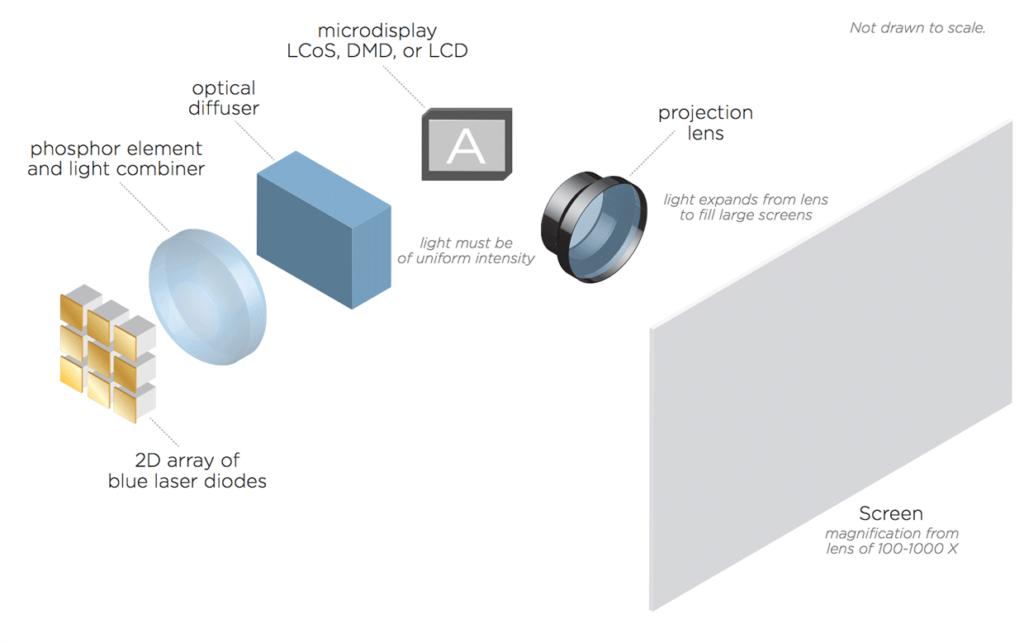
Projectors are a great way to produce an image that is large enough to instruct a classroom or entertain a theater full of moviegoers. There are a variety of projector technologies that are currently available, each with a unique way of producing an image. Regardless of the technology used, all projectors have a few basic components in common.
For a more consumer friendly version, sites like Outdoor Movie HQ and Projector Central are helpful because they compare various specs of projectors and peripherals.
Light Source
There are four primary light sources used in modern projectors. They are:
- High intensity discharge – HID lamps
- Solid-state LED lamps
- Lasers
- Hybrid elimination
High Intensity Discharge Lamps
HID lamps are still the most popular lamps that are used in projectors. These lamps are available in a few different varieties, but mercury vapor and xenon are the most popular HID technologies used in projectors today. Mercury vapor is found in small projectors. These projectors may have multiple lamps to produce the best end result.
There are number of reasons why high intensity discharge lamps are popular. They include:
- Long life: Between 4,000 and 10,000 hours
- Spiky spectrum and red deficient
- Low-power: Between 100 W and 450 W
Xenon is used for larger protectors. Some of its key features include:
- Higher power: Between 500 W and 7000 W
- They have a shorter lifespan of between 500 and 3,000 hours
- They have a wide spectrum that is relatively flat
LED Light Sources
At least three solid-state LEDs are used when they replace other types of lamps. There are red, green, and blue lights that are used. Some LED projectors will include additional lights, such as yellow and magenta, for added spectral channels. LED lights have some advantages over other lamps:
- They offer a wider gamut of colors because they have pure RGB primary colors
- Their operational life can be in excess of 20,000 hours
- They are fast to turn on and quick to warm up
- They do not produce UV light
- Quicker switching between component colors in systems that only have one chip
Lasers
When lasers are used, separate green, blue, and red lasers provide illumination. Laser projectors scan laser beams when producing an image. In most laser projections, the light source illuminates micro display panels.
The primary advantage that lasers have over LEDs or HIDs is that they are more efficient when it comes to collecting light. They have a larger color gamut than LED light projectors.
The downsides of lasers in projection is that they are expensive and a lot of energy has to be expended in cooling the unit.
Hybrid Illumination
As the name implies, this form of lighting combines LEDs and lasers with phosphors to create blue, red, and green lights. There are a number of benefits to this form of lighting technology, including the fact that hybrid projectors are able to achieve in excess of 10,000 lm.
The Light Engine
Video processing and illumination converge at the light engine. Red, green, and blue colors produced by the light source are directed to their respective panels or to the one single panel. The colors are modulated to correspond to the image data that has been transmitted to the panel or panels.
The images that have been modulated are then recombined and create a full color image. This image is magnified and projected onto a wall or screen. The light engines used in a projector are going to vary, depending on the technology used in the display panel. Popular forms of display panel technology include:
- DLP
- LCD
- Lcos
- Three chip DLP
How DLP Works
DLP technology is based on a chip called the Digital Micromirror Device (DMD). This device has between 400,000 and 9,000,000 aluminum square panels. One panel for each pixel. In devices that are currently on the market, the pixel pitch has a size of approximately 1/10 to 1/5 of the diameter of a human hair.
Each mirror sits on top of a hinge that allows it to flip to either side of perpendicular. DMD’s have been referred to as true digital devices. This is because each mirror can only be tilted to 10 or 12 degrees from perpendicular.
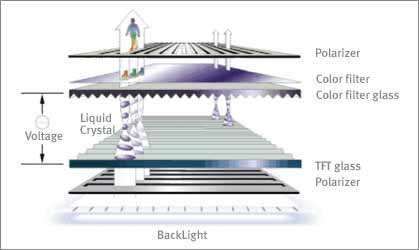
Pros and Cons of LCD Technology
Liquid Crystal Display technology is the least expensive panel technology. The downside of this technology is the images smearing. This may happen during fast motion if the liquid crystal material does not respond fast enough.
- LCD absorbs light. This can lead to photo degradation of the liquid crystal material from ultraviolet. In recent years, this problem has been addressed by using inorganic alignment layers.
- LCD has a lower contrast ratio than DLP or LCoS technology. This is because the pixels in LCD are never fully off.
- Since LCD is driven by analog voltages, there is a greater chance of non-uniformity with both gray scale and color images.
- The “Screen Door Effect,” or the obvious appearance of pixels, is more likely with LCD technology as a result of the low field factor.
Image Projection
There are a number of elements that make up typical projection lenses. Glass is used because of its ability to prevent thermally induced distortion. Lenses are over sized, allowing for horizontal and vertical image shift. In most cases, stepper motors or DC motors are used by the lens mount to control image shift. Zoom and focus are usually controlled by motors on the lens.
MTS modulation transfer function characterizes the optical resolution of a projection lens. This is the number one performance metric for an optical lens. The MTF curve shows how contrast will change with spatial frequency. The performance of the lens is the primary contributor to the overall resolution of the projector. It plays a key role in the image quality and contrast.
Although they are relatively small and look simple, there are a number of components that work together to make a projector function. In this article, we have just scratched the surface. The three key components are:
- Light source
- Image engine
- Image projection (the lens)
In future posts, we will discuss these features as well as other projector components in more detail. Please leave your questions or comments in the comments section below.